Recover
Recover Your Damaged CDs
I learn an old technique to how to recover damaged or scratched disks
with some lost of data. Here we cover some special technique of how to create a full working CD from the scratched one.
First some tools will be needed:
1. Alcohol 120%
2. UltraISO
3. Windows XP/2000 (not tested on 95/98/me)
3. Small piece of cotton
4. Dry cleaner paper
5. Finally, oil for cooking.
First step – preparing the CD
Get the cotton and drop some water, start cleaning vertically the surface of CD.
Do it 3 times and dry the water with a piece of dry cleaner paper. With a new piece
of cotton, drop some oil for cooking and start to wet the surface like you are
washing the CD with the oil. Dry carefully now. Some particles of oil will stay on the
micro surface of the scratch. It’s okay. Seems the oil helps the laser of the CD/DVD driver
to read the surface again. Sure this will work with small unreadable scratchs – some hard
scratches loose parts of the surface of the CD where we have data and it’s lost forever.
But if it is loosed try anyway. With this tip 80% of the small scratched CD’s could be
recovered.
Second Step – testing the CD
With Alcohol 120% make an ISO – image making wizard – and lets see if the app can
read the loosed surface. In my case Alcohol 120% had recovered 60% of the data.
This is not enough. Have tryed other appz, they do not recover all the data. But the
CD/DVD driver laser CAN recover all data in this case. the data is still there, what we do?
Third step – making the new CD
With the main copy system of windows explorer you can do it. Just create one folder
with the same name of the CD label for future burn reference, and copy the CD content
to the folder. When the CD copy process find the scratch, in majority of the cases, it’s
slow down the reading and will recover ALL loosed data.If not, it just tell you there’s
an unreadable sector. In this case your CD is lost. But it’s not my case, finally
windows explorer got all the data from the scratch and made a copy in the folder.
with the ultraISO, wrote the original CD label, drop the content of the folder and
save as Iso. You can Test the new CD just mounting the iso in the Alcohol 120%. In my
case i did ISO of the two discs from MAX PAYNE 2 and tested installing from the mounted
ISO. Works like a charm. I got the 4 mb lost again. So, I have burned the CD and now i
have a working copy from the scratched one.
Sounds too bizzarre, but works. Course you can jump the cleaning process and try to copy
the content with Windows explorer. But in my case did not work without oil…
Ntfs Cluster Size, better harddrive performance
Cluster is an allocation unit. If you create file lets say 1 byte in size, at least one cluster should be allocated on FAT file system. On NTFS if file is small enough, it can be stored in MFT record itself without using additional clusters. When file grows beyond the cluster boundary, another cluster is allocated. It means that the bigger the cluster size, the more disk space is wasted, however, the performance is better.
So if you have a large hard drive & don’t mind wasting some space, format it with a larger cluster size to gain added performance.
The following table shows the default values that Windows NT/2000/XP uses for NTFS formatting:
Drive size
(logical volume) Cluster size Sectors
———————————————————-
512 MB or less 512 bytes 1
513 MB – 1,024 MB (1 GB) 1,024 bytes (1 KB) 2
1,025 MB – 2,048 MB (2 GB) 2,048 bytes (2 KB) 4
2,049 MB and larger 4,096 bytes (4 KB) 8
However, when you format the partition manually, you can specify cluster size 512 bytes, 1 KB, 2 KB, 4 KB, 8 KB, 16 KB, 32 KB, 64 KB in the format dialog box or as a parameter to the command line FORMAT utility.
The performance comes thew the bursts from the hard drive. by having a larger cluster size, you affectively have a larger chunk of data sent to ram rather than having to read multiple smaller chunks of the same data.
Backing Up the Registry
Backing up your registry from time to time is a pretty good idea. Well, there’s an easy way!
For Win 98 & ME…
1. Click Start /Run and type in “regedit” (no quotes).
2. Next, click the Registry menu, Export Registry File …
3. Select a location from the resulting box and give your backup registry a
name. I use:
like this…Regbackupfile14-11-2006.
That’s it! All backed up.
For XP users…
1. Click Start /Run and type in “regedit” (no quotes).
2. Next, click the File menu, Export
3. Select a location from the resulting box and give your backup registry a
name. Something like:
Regbackupfile14-04-2007.
Just a quick note: by default, Windows backs up the registry when you shut down your machine. The above is probably best used for those (like myself) who like to tinker with registry settings.
Now, how to restore the registry you just backed up…
First, if Windows gets an error when loading your registry, it will automatically revert to its backup, so it should never give you any kind of trouble loading.
OK, but what do you do if you’ve been playing around in your registry and have *really* messed stuff up?
Click the Registry menu (in the Registry Editor) and select Import Registry . Then just point the computer to your back up file.
Oh, one more thing. You can also add the registry to your regular backup routine (you do have a backup routine, don’t you?). Your registry is in two hidden files called “User.dat” and “System.dat”, located in the Windows folder. Just add those two files to your normal backup.
Computer Acronyms
ADSL – Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
AGP – Accelerated Graphics Port
ALI – Acer Labs, Incorporated
ALU – Arithmetic Logic Unit
AMD – Advanced Micro Devices
APC – American Power Conversion
ASCII – American Standard Code for Information Interchange
ASIC – Application Specific Integrated Circuit
ASPI – Advanced SCSI Programming Interface
AT – Advanced Technology
ATI – ATI Technologies Inc.
ATX – Advanced Technology Extended
— B —
BFG – BFG Technologies
BIOS – Basic Input Output System
BNC – Barrel Nut Connector
— C —
CAS – Column Address Signal
CD – Compact Disk
CDR – Compact Disk Recorder
CDRW – Compact Disk Re-Writer
CD-ROM – Compact Disk – Read Only Memory
CFM – Cubic Feet per Minute (ft�/min)
CMOS – Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
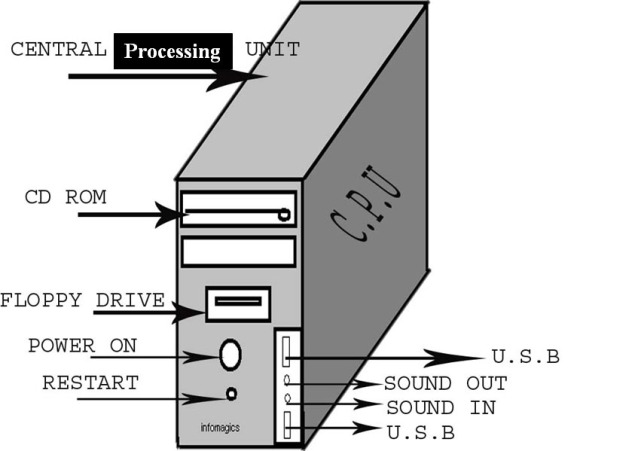
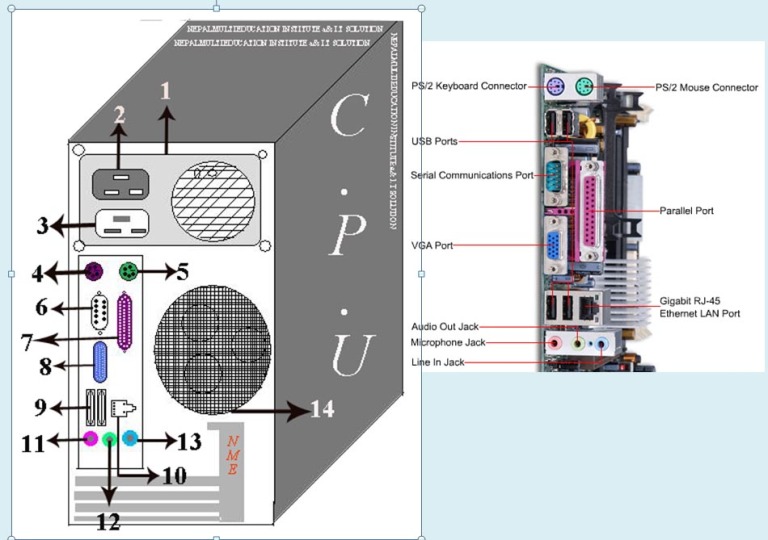
CPU – Central Processing Unit
CTX – CTX Technology Corporation (Commited to Excellence)
— D —
DDR – Double Data Rate
DDR-SDRAM – Double Data Rate – Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory
DFI – DFI Inc. (Design for Innovation)
DIMM – Dual Inline Memory Module
DRAM – Dynamic Random Access Memory
DPI – Dots Per Inch
DSL – See ASDL
DVD – Digital Versatile Disc
DVD-RAM – Digital Versatile Disk – Random Access Memory
— E —
ECC – Error Correction Code
ECS – Elitegroup Computer Systems
EDO – Extended Data Out
EEPROM – Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
EPROM – Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
EVGA – EVGA Corporation
— F —
FC-PGA – Flip Chip Pin Grid Array
FDC – Floppy Disk Controller
FDD – Floppy Disk Drive
FPS – Frame Per Second
FPU – Floating Point Unit
FSAA – Full Screen Anti-Aliasing
FS – For Sale
FSB – Front Side Bus
— G —
GB – Gigabytes
GBps – Gigabytes per second or Gigabits per second
GDI – Graphical Device Interface
GHz – GigaHertz
— H —
HDD – Hard Disk Drive
HIS – Hightech Information System Limited
HP – Hewlett-Packard Development Company
HSF – Heatsink-Fan
— I —
IBM – International Business Machines Corporation
IC – Integrated Circuit
IDE – Integrated Drive Electronics
IFS- Item for Sale
IRQ – Interrupt Request
ISA – Industry Standard Architecture
ISO – International Standards Organization
— J —
JBL – JBL (Jame B. Lansing) Speakers
JVC – JVC Company of America
– K —
Kbps – Kilobits Per Second
KBps – KiloBytes per second
— L —
LG – LG Electronics
LAN – Local Are Network
LCD – Liquid Crystal Display
LDT – Lightning Data Transport
LED – Light Emitting Diode
— M —
MAC – Media Access Control
MB � MotherBoard or Megabyte
MBps – Megabytes Per Second
Mbps – Megabits Per Second or Megabits Per Second
MHz – MegaHertz
MIPS – Million Instructions Per Second
MMX – Multi-Media Extensions
MSI – Micro Star International
— N —
NAS – Network Attached Storage
NAT – Network Address Translation
NEC – NEC Corporation
NIC – Network Interface Card
— O —
OC – Overclock (Over Clock)
OCZ – OCZ Technology
OEM – Original Equipment Manufacturer
— P —
PC – Personal Computer
PCB – Printed Circuit Board
PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnect
PDA – Personal Digital Assistant
PCMCIA – Peripheral Component Microchannel Interconnect Architecture
PGA – Professional Graphics Array
PLD – Programmable Logic Device
PM – Private Message / Private Messaging
PnP – Plug ‘n Play
PNY – PNY Technology
POST – Power On Self Test
PPPoA – Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM
PPPoE – Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet
PQI – PQI Corporation
PSU – Power Supply Unit
— R —
RAID – Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks
RAM – Random Access Memory
RAMDAC – Random Access Memory Digital Analog Convertor
RDRAM – Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory
ROM – Read Only Memory
RPM – Revolutions Per Minute
— S —
SASID – Self-scanned Amorphous Silicon Integrated Display
SCA – SCSI Configured Automatically
SCSI – Small Computer System Interface
SDRAM – Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory
SECC – Single Edge Contact Connector
SODIMM – Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module
SPARC – Scalable Processor ArChitecture
SOHO – Small Office Home Office
SRAM – Static Random Access Memory
SSE – Streaming SIMD Extensions
SVGA – Super Video Graphics Array
S/PDIF – Sony/Philips Digital Interface
— T —
TB – Terabytes
TBps – Terabytes per second
Tbps – Terabits per second
TDK – TDK Electronics
TEC – Thermoelectric Cooler
TPC – TipidPC
TWAIN – Technology Without An Important Name
— U —
UART – Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
USB – Universal Serial Bus
UTP – Unshieled Twisted Pair
— V —
VCD – Video CD
VPN – Virtual Private Network
— W —
WAN – Wide Area Network
WTB – Want to Buy
WYSIWYG – What You See Is What You Get
— X —
XGA – Extended Graphics Array
XFX – XFX Graphics, a Division of Pine
XMS – Extended Memory Specification
XT – Extended Technology
Safely Editing The Registry
Windows XP has a vast number of configuration dialogs, but some adjustments can be performed only by directly editing the Registry. Frequently, tips involving Registry tweaks include stern warnings to back up the Registry before making any change. The Windows XP Backup applet can back up the Registry along with other elements of the System State, but the resulting data file can occupy hundreds of megabytes. You’re better off saving a system restore point each time you’re about to edit the Registry. Better still, you can use Regedit to back up only the Registry keys that will be changed.
Click on Start | Run and enter Regedit to launch the Registry editor. To back up an individual key you plan to edit, navigate to the key and right-click on it. Choose Export from the menu, and save the key to a REG file. Open the REG file in Notepad and insert a few comment lines that describe the source and purpose of the tweak. (To create a comment line, simply put a semicolon at the start of the line.)
Now go ahead and make all the changes to Registry keys and values specified by the tip you’re applying. Any time you add a new key or value, make a note of it with another comment line in the REG file. When you’re done, save the REG file and close Notepad.
If later you want to undo this Registry tweak, just double-click on the REG file and confirm that you want to add it to the Registry. This will restore any deleted keys or values and will restore the original data for any values whose data was changed. Note that this will not remove new keys or values that were added; that’s why you need to make comments about such changes.
Right-click on the REG file and choose Edit, which will open it in Notepad. Check for comments about keys or values that were added, and if you find any, use Regedit to delete them. You can delete the REG file itself once you’ve completed this process
FULL FORM OF SOME WORD
AC : alternating current
ALR : Advanced Logic Research
ABM : Atanasoft Berry Computer
ALU : arithmetic logical unite
AT : advanced technology
ATX : advanced technology extended
AFT : Automatic Fine Tuning
AF : Audio Frequency
AM : Amplitude Modulation
AGC : Automatic Gain Control
AFC : Automatic frequency control
AVC : Automatic Volume Control
AVI : Audio Video Grope
ATM : Automated Teller Machine
BHT : Boosted High Tension
DNS : Domain Name Server
DHCP : Dynamic Host Configure Protocol
C/S : Cycle per Second
CRT : Cathode Rey Tube
CTV : Color Television
CVT : Constant Voltage Transformer
CDMA : Code Division Multiple Access
BIT : Binary digit
BCC : Blind Carbon Copy
BIOS : Basic input output system
BPI : Bytes per inch
CD : compact disk
CC : Carbon Copy
CD-ROM : Compact disk read only memory
CD-RW : Compact disk Re-writer
CPU : central processing unite
CU : control unite
COM. : Commercial/Component Object Model
CMOS : Complementary Metal Oxide semiconductor
CAD : computer aided design
COBOL : Common Business Oriented Language
DC : direct current
CGA : coloured graphics adapter
DOS : Disk operating system
DVD : Digital video/versatile disk
DNS : Domain Name Server
DRAM : Dynamic RAM
ENIAC : Electronic Numerical Integrator
and Calculator
EDSAC : Electronic Delay Storage AutomaticComputer
EDVAC : Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic
Computer
E-commerce : Electronic commerce/business
E-mail : Electronic mail
EICAS : Engine Indicator and crew Alert system
EPROM : Erasable programmable ROM
PROM : programmable ROM
EGA : enhanced graphics adapter
FM : Frequency Modulation
FDD : floppy disk drive
FTP : File Transfer Protocol
FMC : Flight management computer
GB : Giga Byte
GHz : Giga hertz
GUI : Graphical User Interface
HDD : Hard disk drive
HTTP : Hypertext Transfer Protocol
HTML : Hypertext Markup Language
HLCIT : High Commission for Information Technology
I/O : Input/output
IBM : International business machine
IC : Integrated circuit
ISO : international standard Organization
ISP : Internet Service Provider
IP : Internet Protocol
IT : Information Technology
CISC : Complex Instruction set computer
JPEG : Joint Photo Export Group
KB : kilo byte
LAN : local area connection
LSI : Large Scale Integration
LCD : liquid crystal display
MAN : Metropolitan area network
MB : mega bytes
MHz : mega hertz
Ms. : Microsoft
Ms-Dos : Microsoft disk operating system
MBA : Master Business Administration
MPEG : Moving Picture Export Group / Motion Picture Export Group
MSI : Medium Scale Integration
MOS : Metal Oxide semiconductor
MODEM : Modulator and Demodulator
MDA : monochrome display adapter
MCGA : multicolour graphics adapter
NCR : National capital Region
NCC : National Computer Center
NME : Nepal Multi Education
NAC : Nepal Airlines corporation
NIC : Network Interface Card
OS : Operating system
OSI : Open System Interconnection
OCR : Optical character recognition
PC : personal computer
PCB : Printed Circuit Board
PDF : Portable Document Format
POP : Post Office Protocol
PS/2 : Personal System/2
POS : Point Sales Terminal
RAM : Random access memory
RISC : Reduced Instruction Set computer
SMPS : Switch Mode Power Supply
SMTP : Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
SRAM : Static Read only memory
SDRAM : Synchronous Dynamic RAM
SVGA : Super video graphics array
TB : Terabyte
TT : Typing Tutor
TCP : Transfer Configure protocol
TUI : Text User Interface
TFT : Thin Film Transistor
UPS : Uninterrupted Power Supply
UNIVAC : Universal Automatic Computer
URL : Uniform Research Locater
ULSI : Ultra Large Integration
ULSIC : Ultra Large Scale Integration Circuit
VDU : Visual Display Unite
VISA : Visitor Intention stay aboard
International Service Associations
VLSI : Very Large Integration
WHO : World Health Origination
WWW : World Wide Web
WAN : Wide Aria Network
XT : Extra/Extended Technology
Introduction of Special Key
~ = Tiled key
! = Exclamation
@ = At the rate
# = Hash
$ = Dollar
% = Percentage
^ = Carat
& = And
* = Asterisk or star mark
( ) = Parentheses
– = Dash
_ = Underscore
| = Vertical mark or pipeline
; = Semicolon
: = Colon
‘…’ = Single quite mark (smart)
“…” = Double quite mark (smart)
‘ = Single quite (straight),Apostrophe
” = Double quite mark (straight)
Inverted Kamas
/ = Forward Slash
\ = Back slash
= Back Space
< = Less than
> = Greater than
= Arrow key
= Enter key
. = Dot (Full Stop)
Application file name of some programs:
typshala.exe : Typical typing programs
tt?.Exe/tt.exe : typing tutor
wordpad.exe : simple word processing Program (word pad)
notepad.exe : simple word processing program (note pad)
calc.exe : calculator
mspaing.exe : Microsoft paint
command.com : dos prompt
winword.exe : Microsoft word
excel.exe : Microsoft excel
powerpnt.exe : Microsoft power point
Msaccess.exe : Microsoft access
pm65.exe/pm70.exe : adobe PageMaker 6.5/7.0
coreldrw.exe : Corel draw
photoshp.exe
photoshop.exe : adobe Photoshop 6.0/7.0
msoffice.exe : shortcut bar
frontpg.exe : Microsoft front page
charmap.exe : character map
mplayer.exe
wmplayer.exe
wmplayer2.exe : media player
cdplayer.exe : cd player
explore.exe : windows Explorer
flash.exe : freehand flash
iexplore.exe : Internet Explorer
msimn.exe : Outlook express
SYSTEM SURTCUT KEY
Close : Alt+f4, Alt +spacebar +C
Close Windows : Control+Q
Restore down : Alt +spacebar +R
Maximize : Alt +spacebar +X
Minimize : Alt +spacebar +N
Shutdown : windows logo +UU
Restart : windows logo +U+R
Stand by : windows logo +U+S
Lock : windows logo +L
Log off : windows logo +LL
Run : windows logo +R
Computer open : windows logo +E
Search : windows logo +F
NEPAL MULTI EDUCATION INSTITUTE & I.T SOLUTION E-mail: rohitmc6@gmail.com 9847897410 460029
Prepared by Rohit mahatara chhetri Dharmawoti-1 Bagdula pyuthan
Web Site : https://nmeiit.wordpress.com/
- Posted in: Rohitmc6@gmail.com